Ear Infection
Ear infection or acute otitis media is a condition caused by bacteria or viruses that affect the middle ear. The infection occurs more commonly in children. Ear infections are characterized by fluid buildup and inflammation in the middle ear and can lead to significant pain and discomfort. Ear infectionstypically subside by themselves. Treatment may be administered to alleviate the pain and manage the symptoms however. Antibiotic treatment may be necessary in case of severe ear infections or infections that occur in babies. In some cases severe or persistent ear infections caused by constant fluid buildup in the middle ear can lead to problems in hearing and other complications.
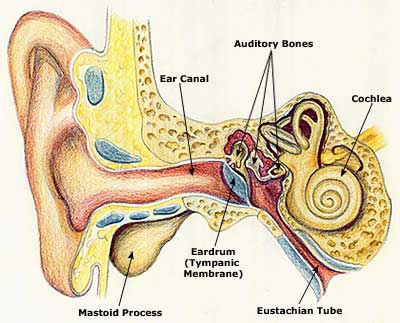
Symptoms of Ear Infection
The common signs and symptoms of a ear infection are as follows:
In Children
- Pain in the ear which may worsen while lying down
- Tugging at the ear
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Persistent crying
- Irritability
- Headache
- Poor response to sounds
- Loss of balance
- Appetite loss
- High fever
- Drainage of fluid
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
In Adults
- Pain in the ear
- Sore throat
- Fluid drainage
- Problems in hearing
- The symptoms persist for more than one day
- The pain is severe
- There is fluid, pus or blood discharge from the childs ear
- The child seems irritable after a cold or other respiratory infection
The symptoms of a ear infection may sometimes be indicative of other underlying conditions. Therefore it is better to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and early treatment especially if such symptoms are observed in children. Seek prompt medical attention in case of the following:
Causes for Ear Infection
The common causes of a ear infection are as follows:
- Ear infection occurs when bacteria or viruses affect the middle ear. Ear infections are usually associated with other conditions such as a common cold, allergies or upper respiratory infections. Such illnesses result in nasal congestion and swelling of the membranes in the nose, throat and Eustachian tube. The Eustachian tube extends from the middle ear to the throat. It is involved in protecting, aerating and draining the middle ear. The tube can get blocked when there is inflammation or swelling. Mucus buildup in the Eustachian tubes on account of an upper respiratory infection can also cause a blockage. These conditions can cause fluid to collect in the middle ear. When bacteria or viruses infect this fluid, an ear infection occurs. The Eustachian tubes in children are narrow and lie more horizontally. This makes drainage slightly more difficult and hence they get blocked easily.
- The adenoids are small tissue masses that are located at towards the back of the throat. They aid in the immune response of the body which also means that they are affected each time they respond to an infection. The adenoids are located quite close to the Eustachian tube openings.
- Abnormalities or dysfunction of the Eustachian tube can allow fluid buildup to continue even after an infection subsides.
- If there is a tear in the eardrum due to various causes, an ear infection can persist for long periods of time.
- Children aged 6 months to 2 years are more prone to ear infections due to the size and shape of the Eustachian tubes. The immune system is not fully developed in children and this can also make them more vulnerable to infections.
- Children in group child care are more prone to ear infections.
- Babies who bottle feed are more susceptible to ear infections than babies who are breast fed.
- Ear infections are seen to occur commonly during seasons when the flu and colds are prevalent.
- Individuals who are exposed to smoke or pollution may suffer from ear infections more commonly.
- The risk of developing ear infections may run in families.
- Hearing loss
- Impairment in speech or development in infants
- Spread of the infection to the tissues of the skull and maybe even the brain
Therefore when they become enlarged or inflamed, they may block the Eustachian tubes. The adenoids are larger and more active in children and hence pose a greater risk of ear infections.
There are certain risk factors which that can make an individual susceptible to ear infections. These include:
In most cases, ear infections do not lead to any complications. However recurring or severe infections may result in some long-term problems. These include:
Remedies for Ear Infection
Minor ear infections can be treated quite effectively at home with over the counter medications or home remedies. Not all home remedies are scientifically investigated however, so while some remedies may be highly effective, others may be of not much help. For this reason it is important that you closely monitor the condition and if there is no response to treatment within a couple of days make it a point to seek medical attention. Here are some natural remedies and tips that you can use to treat ear infections:
- It is important to avoid putting cotton swabs or other instruments inside the ear when there is an infection. This can lead to damage of the eardrum and may worsen the infection.
- Keep the ear clean and dry at all times
- If you need to blow your nose, do so gently to avoid putting pressure on the eardrum.
- Avoid exposure to smoke.
- Place a small piece of cotton in the ears to protect the ear from pollution and other irritants whilst outdoors.
- A warm compress is one of the most effective home remedies for inner ear infections. Place a warm washcloth next to the affected ear. You can also use a heating pad. You can even use cold compresses to alleviate swelling and discomfort. Keep an ice bag near the affected ear for some time.
- Keep your head elevated while sleeping by placing a pillow underneath. This will enable drainage of the Eustachian tubes.
- Yawning helps to open up the Eustachian tubes by contracting the muscles.
- Use a decongestant if you suffer from ear problems due to the cold. However consult your doctor before taking any such medication.
- Taking a hot shower Tcan also help, as the steam will help to unblock the ear.
- Home remedies for ear aches also include holy basil. Take some holy basil leaves and extract the juice from them. Place a couple of drops areain the affected ear. This will relieve ear pain and reduce infection.
- Garlic helpfulcan serve as an extremely effective remedy for a variety of ear infections . Boil two or three garlic cloves in water. Crush them and add some salt. Put the mixture in a piece of clean cloth and place against the affected area. You can even add a few drops of garlic juice to the affected ear, using it as you would with ear drops. Garlic is noted for its antimicrobial properties that make it highly effective, and most studies have supported these claims.
- To protect the ears while swimming, add some mineral oil to the ears before entering the water. However it is best to avoid swimming until the infection clears up.
- A common home remedy for ear infections is hydrogen peroxide. Add a few drops inside the affected ear for relief from the symptoms.
- Vitamin C helps to strengthen the immune system. It has antibiotic properties and helps to prevent inflammation.
Diet for Ear Infection
Take vitamin C to boost your immune system, it will help you to combat infection. Increase Zinc intake, it reduces ear infection. Eat a healthy diet with lots of calcium in it. Avoid processed foods and hydrogenated oils. Stress on breast feeding for infection in infants.
Suggestions for Ear Infection
Use the following tips preventingto prevent ear infections:
- Maintain good hygiene by washing your hands frequently so that you illnessescan avoid the risk of contracting an infection through the transference of germs via contact.
- Avoid exposure to smoke including second-hand smoke
- Breast-feed your baby, as breast milk contains antibodies that help to protect babyyour infant from infections.
- Hold your baby in an upright position during feedings.
- Have your child vaccinated regularly.
References
- Klein JO. Management of acute otitis media in an era of increasing antibiotic resistance. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1999 Oct 5;49 Suppl 1:S15-7. PubMed PMID: 10577768.
- Pai ST, Platt MW. Antifungal effects of Allium sativum (garlic) extract against the Aspergillus species involved in otomycosis. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1995 Jan;20(1):14-8. PubMed PMID: 7765862.
- Advice for earache: I’m having trouble with my right ear. it itches then it's gets really sore i recently had a ear infection it seems to of cleared up now but my ear is causing pain. Pls advice.
It is very important to treat the ear infection to avoid ear pain. Apply warm moist heat... - Natural cure for ear infection: I think I have an ear infection, but I don't have insurance, so if I don't get it treated will it just go away without causing any permanent damage? What's the best home cure?
You don't seem to be clear about the fact, as to whether you are suffering from an infection... - Cures for ear infection: i wanted to know how to cure a ear infection without going to the doctor. everybody relies on a doctor and i would like to know how to cure it without a doctor
Some home cures for ear infection are: Garlic cloves- Warmed and mash with salt. Wrap in a... - Natural cures for ear infections: how do i cure ear infections naturally?
In a young child, chronic ear infections may result from both structural as well as... - Advice on ear infections: Are ear infections contagious?
The bacterial present in the ear which cause the ear infection are not contagious. But the cold...
lay down and turn head sideways and fill ear w/hydrogen peroxide. leave it in for about 8 min and then turn head and let peroxide drain out of ear- while doing the other ear. the peroxide boils & looses everything bad in your ears.
Slice an onion in half and grill in pan until hot. cover with paper towel and apply cut side down to ear. the onion will draw out the infection and help to alleviate pain in the ear almost immediately.
never put olive oil into an ear that is giving pain as the pain usually means there is infection present and olive oil can make it worse.oil should only be used to soften wax.
I have used Hydrogen Peroxide all my life for ear infections. Its only recent that physicians are adapting the same technique. Tilt your head sideways and pour the peroxide into your ear and let it stay in until it stops fizzing, then turn your head over a towel and drain it out. This will insure that all infection is dead. Repeat again after you pour out the first treatment.